Getting Started - No Scripting
Please Note: This page is a work in progress and may not be 100% correct or complete. If you have any questions or need for clarification please ask! Questions are welcome and will help make this guide better. And there is no need for coding knowledge to do any of the things listed in this part of the guide.
Contents
starting a new world
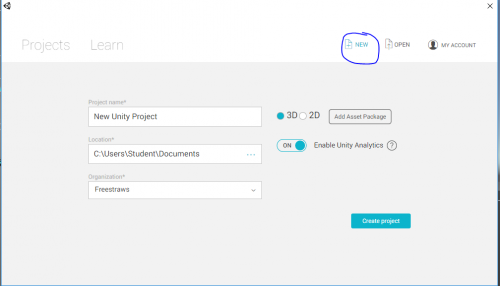
Make an account at https://unity3d.com/, Unity will probably ask you to sign in before you start doing anything with their application. Once you've done that and signed in, you can go to 'New' and see something like this:
You don't need to worry about Unity Analytics or Asset Packages yet, and this guide is for making 3d games with the Unity engine, so keep that option checked. Press 'Create project'.
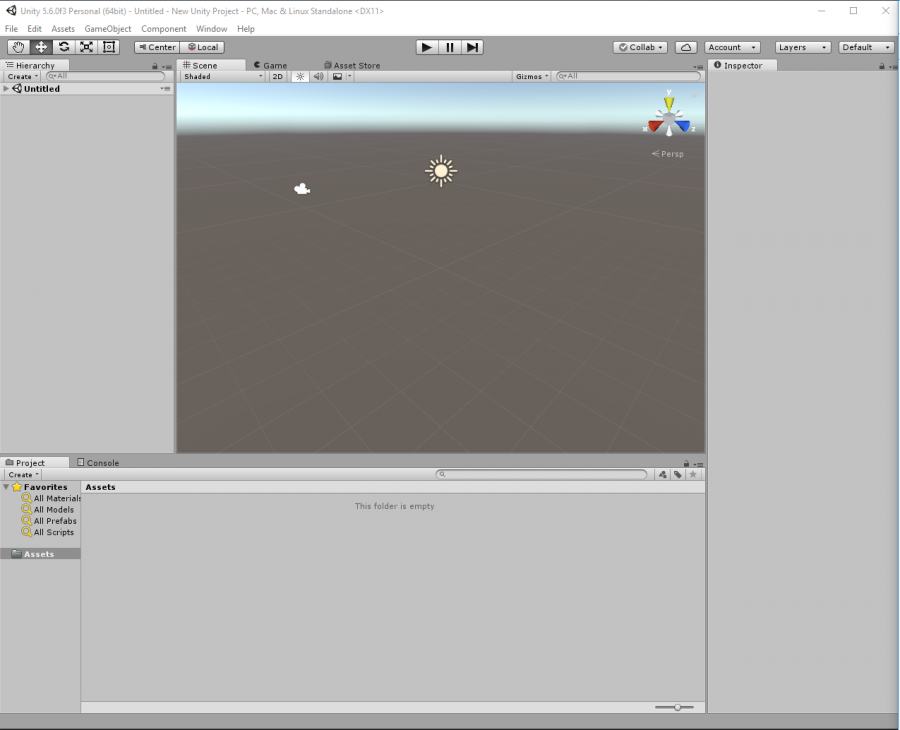
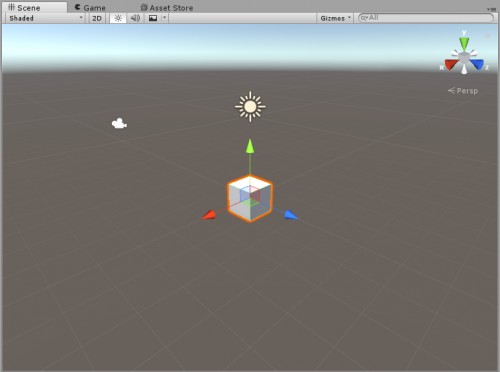
You should now be looking at something like this:
overview of editor and various tabs
There's a lot of UI here whose functionality may or may not seem obvious to you, so I will try to explain what each piece is for.
placing things in a scene
primitive 3d objects
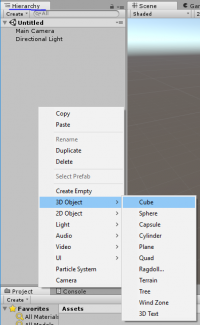
2 ways to start to place primitive 3d shapes in a scene: Right-click in the Hierarchy tab (the other way is almost the same but starts with going to GameObject at the top of the screen instead of right-clicking),
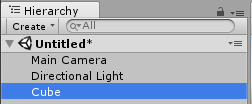
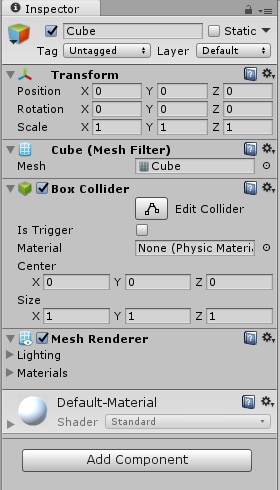
Two things happen: one, a cube is added to the lists of objects in the hierarchy tab, and two, you should now see a cube in the Scene tab/viewer:
and if the cube has an orange outline, as shown in my scene tab, there should also be some new information in the Inspector tab:
Manipulating things in this tab is very important, for example it allows one to move, rotate, or scale something in specific ways. This can also be achieved in the Scene tab, when you have an object selected you can move, rotate, or scale it along the x, y, or z axis by adjusting the red, green, or blue axes respectively.
Some tips/ shortcuts for object manipulation:
- While in scene view and manipulating objects you may also find it useful to use some shortcuts: W gets the handles for position, E gets you to rotation manipulation, and R is for scaling.
- T is also a shortcut for object manipulation, the center O lets you move the object around wherever the mouse is, and you can also scale scale from corners or sides of things individually (instead of scaling from the center point of the object on the axis you're working with, which is how it usually works).
- Q just lets you move around the scene in the view, which can be very useful.
- F focuses in on whatever object you have selected.
- ctrl-D duplicates the selected object.
- Right-clicking and moving the mouse allows you to rotate your view in the scene. Ctrl middle-click allows translation of the camera position.
lights
To add a light to a scene, you would go to GameObject > Light and select one of the following kinds of lights to add:
spotlight: Exactly like it sounds, it's a cone of light for which you can specify the spot angle, range, intensity, and color. There are of course other setting you can see in the inspector but those 4 are the most important. All of these can be adjusted based on variables with scripting. Light doesn't really go past the given range, even when you might feel like it should. Spot angle corresponds to how wide you want the cone of light to be. Intensity is a range of how bright the light is, 0 being that it emits no light, and 1 being the brightest it can possibly be.
point light: Very similar to the spotlight except that instead of the light brightening an area in a cone shape, point lights are a sphere of light going from the center of the object to the specified radius in every direction.
directional light: typically used for lights that affect an entire scene, like a sun or moon. There is no range for this type of light because it's meant to be global. If you want shadows, pick Shadow Type > Soft Shadows (or Hard Shadows, try them both and decide which on is better for your project). You usually only want to have 1, or 2 if you want something like a day/ night cycle, of these in a scene.
area light: This one is not used nearly as often as the 3 above, but for lighting rooms evenly this can be an extremely useful tool.
A more thorough explanation of lighting in Unity.
models from your project assets
Asset Store
If you don't already have any assets you want to use and aren't good at 3d modeling, or just want a base asset to edit, I'd highly suggest looking in the Asset Store (you can get to it by going to Window > Asset Store). It has a huge variety of useful scripts, 3d models, audio clips, textures, and shaders, many of which are free. Some assets do cost money, so be mindful of this, read the reviews, look at how frequently it gets been updated, and if it is okay with the your version of Unity. If you do decide to buy an asset, it will be available for any project you decide to do with Unity, and can be imported to other programs too, if you want.
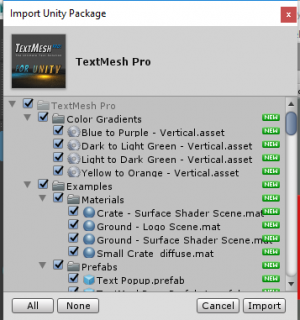
Once you've selected an asset, you can download it from the store window, and then Unity will ask you what parts you'd like to import, it defaults to all but you can deselect folders or specific items from the package.
If you have a model you'd like to import into Unity without the Asset Store, the easiest way to do so is to just drag it from your file manager into the Project tab, which is by default placed below the Hierarchy and Scene + Game tabs. Once you have a model of the right format (see here for a list of Unity compatible file types) find it in the Project tab, and drag it into the Scene or into the Hierarchy. Make sure you know the difference between Scene view and Game view! You can only change things in Scene view, but the Game tab allows you to test how the game actually plays. I will be talking about both of these more later in this guide.
parent/ child hierarchy
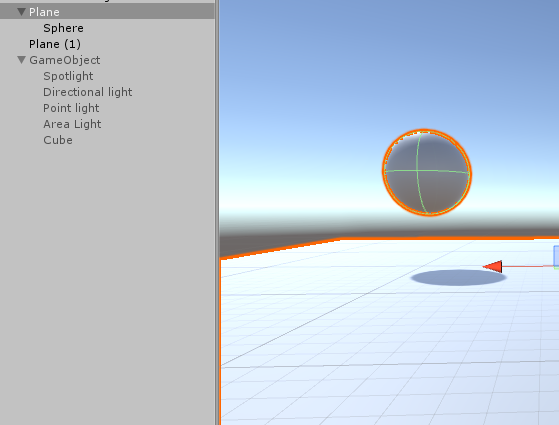
To make an object the child of another, all one has to do is drag the chosen child object in the Hierarchy to the name of the chosen parent object (again in the Hierarchy, this is the only place other than in scripting, that this can be done). Now you might be asking what the point of a parent child object relationship, and aside from organization purposes, child objects keep their position, rotation, and scale in relation to their parent object. So when you move around a parent, the child stays in its relative position from the parent object. See how, in the image below, even if I only have Plane selected in the hierarchy, it looks like both the plane and the sphere are selected in scene view?
This is called local positioning. When an object has no parent it still has a local position, but it is the same as its global position, because every object is a child of the scene or world itself. This becomes important later because you may want to change an object's relative position to a parent and not the global, or maybe you want to edit both, but just make sure you know the difference between an object's local, or relative position and global position. If an object is a child object, the Transform (meaning the position, rotation, and scale) is relative, or local, to the parent object. The same goes for rotation and scale, although you usually only want to change local scale, changing an object's global scale is never a great idea.
how to test things out
 That play button allows one to test everything one has made so far!
That play button allows one to test everything one has made so far!
If Scene and Game are in the same window space, as above, Unity will automatically switch you from Scene to Game. You are still able to edit everything you were able to while not in play mode, so I usually keep Scene and Game in separate windows to see at the same time so I can more easily test things.
play vs edit mode
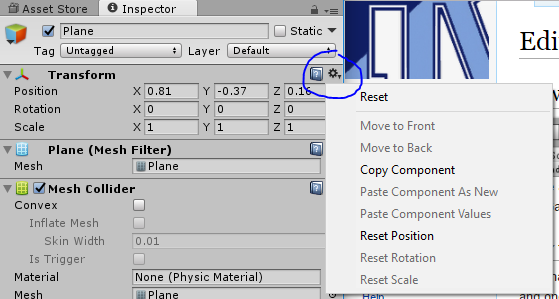
Any changes you make to the world or its objects while in play mode will not get saved! Please keep this in mind. One way around that that I've found is to copy the edited object while in play mode and once you've gone back to edit, you can paste the edited version in and delete the original. As an alternative you can also copy individual aspects of an object (such as the Transform which contains position, rotation, and scale) by finding the relevant part in the Inspector, and clicking the little gear at the top left of every part, otherwise known as a Component.
Note: Changes to scripts are not affected by this limitation, but if you change a script while in play and save it, Unity will reload all its scripts, not just the one you edited, and this may break things, especially things that should only happen when the game first starts up.